Rudolf Diesel (1878) invented an engine. He invented it to solve the problem of engine inefficiencies that the existing engines had. Before then, all vehicle engines used only about 10% of the fuel to move the vehicle. The rest was wasteful heat. By 1892, he patented it for what we now call the diesel engines.
People knew the diesel engine to be notoriously sooty, dirty, and noisy. But just as every other technology developed, the diesel engine also did. In the 21st century, the diesel engine has grown to be cleaner, quieter, and even more efficient.
This article would show you how the Diesel engine works and would answer some questions you have about Diesel engines.
How Does the Diesel Engine Work?
If you are not a science person, don’t be scared to read this session. It’s broken down to the very basics. I would guide you through.
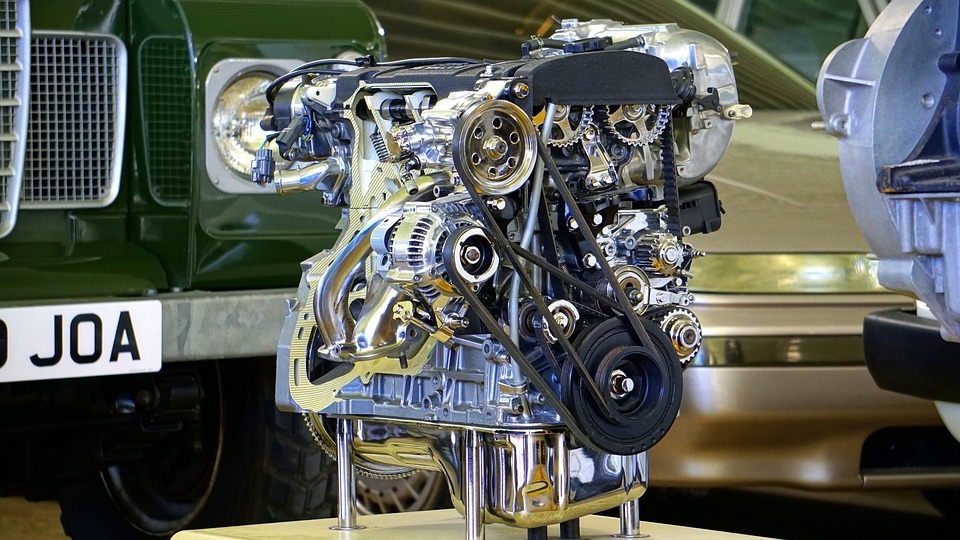
Just as other internal combustion engines, Diesel engines convert chemical energy (from diesel) to mechanical energy. They are the most versatile and economical engines in our world today. It has been serving humanity for more than a century now.
The slider-crank mechanism
The slider-crack transfers the linear motion of the piston to the rotational motion of the crank. You can see the piston moving up and down in the cylinder. And the crank moves rotationally. The rotary movement moves the wheels of your car.
The chemical energy of the diesel is converted to mechanical energy through a four-stroke combustion cycle:
Intake stroke
The piston starts at the top of the cylinder. As it goes downward, it creates a suction pressure in the cylinder. The inlet valve opens, allowing fresh air to be sucked in. It’s like breathing in.
Compression stroke
This stroke begins with the piston at the bottom of the cylinder. During this return stroke, the inlet valve closes. The air in the cylinder gets compressed.
Power stroke
The fuel injector injects an atomized form of diesel into the cylinder. This causes an explosion that pushes the piston to the bottom of the cylinder. It’s in this stroke that the engine converts the chemical energy of the fluid to mechanical energy.
Exhaust stroke
The force at which the piston goes downward creates an upward movement. This pushes out the exhaust created from the combustion through the exhaust valve.
This repeated process keeps your diesel burning and your engine rolling.
Diesel Engine vs Gasoline Engine: Similarities and Differences
Theoretically, the diesel engine and the gasoline engine are very similar. And works in a resembling pattern.
Here are the similarities in design
- They are both internal combustion engines.
- They both convert chemical energy available in the fuel to mechanical energy.
- They both use this mechanical energy to move a piston to and fro inside a cylinder. And it’s converted to rotary motion needed to turn your car wheels.
- They both require the slider crank to function.
Differences in design
In gasoline engines, a spark from the spark plug triggers the combustion. But in Diesel engines, there are no spark plugs. The direct injection of diesel triggers the combustion into the hot air. The heat of the air initiates the combustion of the diesel to start.
Diesel vs Gasoline Engine: Which is Best for You?
Are you contemplating the best engine that would just be right for you? Worry no more. I’ve got your solution in this piece. Your choice of the engine should depend on some factors. I would list those likely factors here and say a little about them. So, you can make a wise decision after all.
For Diesel
1. Fuel efficiency
During the stage of the compression stroke, higher compression leads to better efficiency, more power released, and less fuel used. Because, when the air molecules are closely packed in the cylinder, fuel has a better chance of reacting with as many oxygen molecules as possible. Diesel engines have a compression ratio of 14:1 to 25:1. As compared to gasoline engines, which have a ratio of 8:1 to 12:1.
2. Emission control
If you are environmentally friendly, then this is for you. Modern diesel engines, when compared to gasoline engines, now emit less carbon dioxide into the environment. This helps in keeping the environment clean and safe. Diesel engines do this because they burn less fuel than gasoline engines.
3. Heavy loads
Torque is a force that causes rotation. Just as explained earlier, Diesel engines have more compression ratio. This produces higher torque than gasoline engines.
The more torque an engine has, the more work it can do. This makes the Diesel engine suitable for hauling more loads, whilst consuming less fuel. This is the reason most trailers and trucks use diesel.
4. Longer service interval
Diesel engines are designed to run at a lower speed as compared to gasoline engines. This reduces the threat of wear and tear. Also, the components of the engine are thicker. This is because of the high pressure it always has to withstand. This makes them durable and more resistant to failure.
5. Diesel cars undergo less depreciation
Diesel cars don’t just slowly wear off, they also lose lesser value over the year when compared to the gasoline engine. This is because second-hand diesel cars are usually in demand by Indians. This keeps the price high, even in second-hand states.
Also, diesel is light oil. This means the diesel is capable of lubricating the combustion chamber when you use it. This reduces the chances of wearing and tearing, which means less service is required.
For Gasoline
If diesel engines are more efficient, why do most cars have gasoline engines? Europeans have opened their arms to Diesel engine technology. But most drivers in the USA have nodded their heads away from it. Probably, it could be for the reasons below.
- Diesel engines are more expensive than gasoline
- They are noisier and tend to vibrate.
- Diesel fuel is less readily available than gasoline
- Diesel engines have costlier parts, making the replacement of parts expensive.
- They are harder to start in cold weather.
If it were up to us, more people will use diesel-powered vehicles. But that’s not the case. Probably because gasoline has been the trend for centuries. The diesel engine is an outstanding technology and you should try it.
For Arizonans, your diesel engines are in completely safe hands. Phoenix diesel repair fix and service light and medium diesel trucks, as well as diesel cars. If your engine gets faulty, rest assured we can restore it. Reach out to us.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does a Diesel Engine Work?
Diesel engines convert chemical energy from diesel fuel into mechanical energy through a four-stroke combustion cycle:
- Intake Stroke: Fresh air is drawn into the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke: The air is compressed, raising its temperature.
- Power Stroke: Diesel is injected into the hot air, causing an explosion that pushes the piston down.
- Exhaust Stroke: The piston expels exhaust gases through the exhaust valve. This process repeats, powering the engine and moving the vehicle.
What is the Difference Between a Diesel Engine and a Gasoline Engine?
Both engines are internal combustion types, but the key difference is in how combustion is triggered:
- Gasoline engines use a spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture.
- Diesel engines rely on the heat of compressed air to ignite the injected diesel fuel, which makes them more fuel-efficient and capable of handling heavier loads.
Why Should I Choose a Diesel Engine?
Diesel engines offer several advantages:
- Fuel Efficiency: Diesel engines are more fuel-efficient due to their higher compression ratios.
- Lower Emissions: Modern diesel engines emit less carbon dioxide than gasoline engines.
- More Torque: Diesel engines produce higher torque, making them ideal for hauling heavy loads.
- Longer Service Life: Diesel engines are built to withstand high pressure, offering durability and reduced wear.
- Higher Resale Value: Diesel cars tend to retain their value better over time.
What Are the Drawbacks of Diesel Engines?
While diesel engines are efficient, they come with a few downsides:
- They are more expensive than gasoline engines.
- Noise and Vibration: Diesel engines tend to be noisier and have more vibration.
- Cold Weather Starting: Diesel engines can be harder to start in cold temperatures.
- Fuel Availability: Diesel fuel is not as readily available as gasoline in some areas.
- Costly Repairs: Diesel engines have more expensive parts and maintenance costs.
What Makes Diesel Engines Better for Heavy Loads?
Diesel engines are better for heavy loads due to their higher torque output. Torque is the force that causes rotation, and the higher compression ratio in diesel engines produces more torque. This makes diesel engines ideal for vehicles like trucks and trailers that need to haul heavy loads efficiently.
Are Diesel Engines Environmentally Friendly?
Modern diesel engines are environmentally friendly in comparison to older models. They burn less fuel than gasoline engines, which results in lower carbon emissions. This makes them a more eco-conscious option for those seeking to reduce their environmental impact.